*
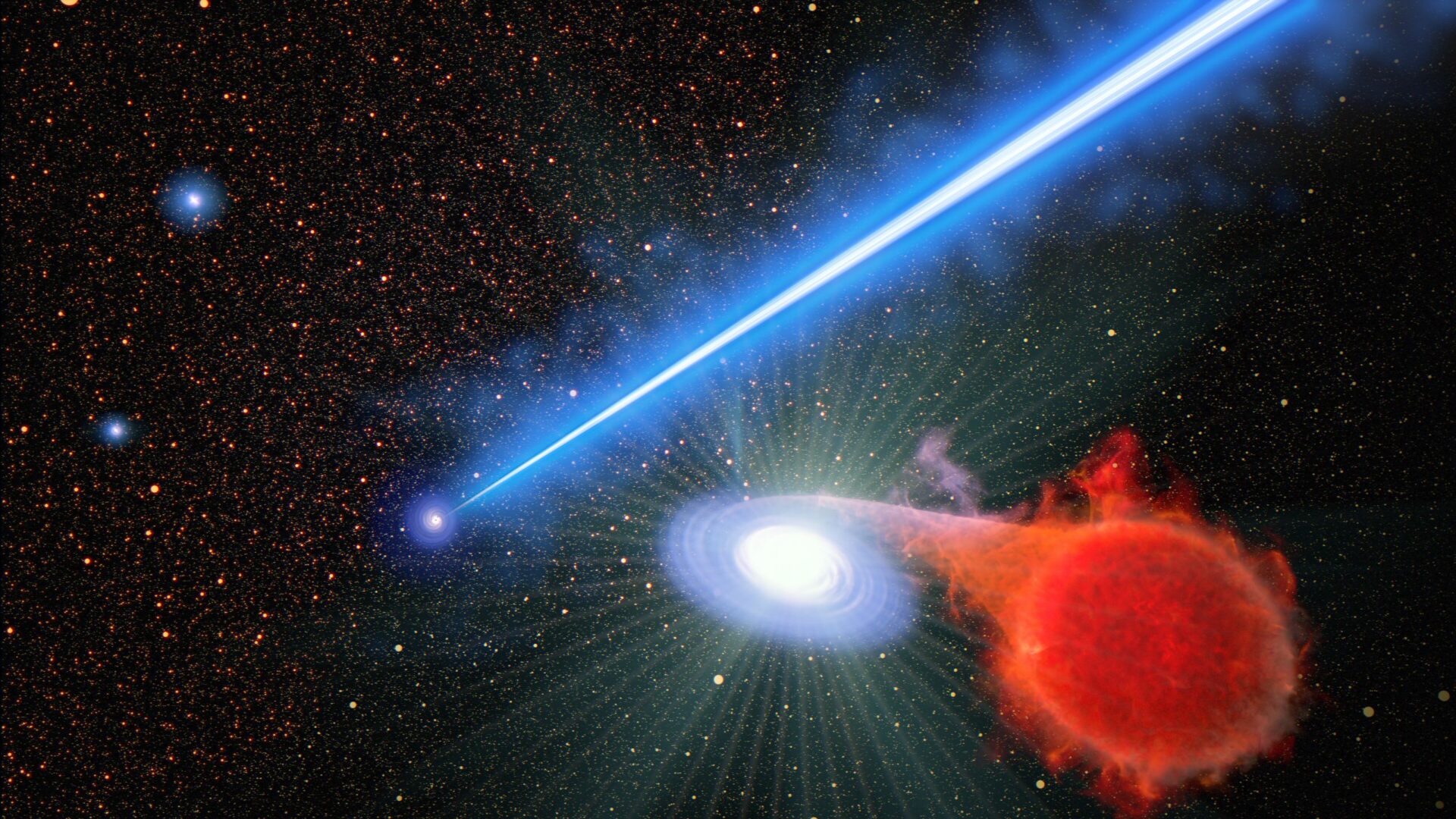
For the reason that Seventies, astronomers have noticed that supermassive black holes (SMBHs) reside on the facilities of most large galaxies. In some instances, these black holes speed up gasoline and dirt from their poles, forming relativistic jets that may prolong for 1000’s of light-years. Utilizing the NASA/ESA Hubble Area Telescope, a staff of astronomers noticed the jet emanating from the middle of M87, the supermassive galaxy positioned 53.5 million light-years away. To their shock, the staff noticed nova erupting alongside the jet’s trajectory, twice as many as they noticed in M87 itself.
The staff was led by Alec M. Lessing, a Stanford College astronomer, and included researchers from the American Museum of Pure Historical past, the College of Maryland Baltimore, Columbia College, Yale College, the SETI Institute, and NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle. The paper detailing their findings not too long ago appeared in The Astrophysical Journal. Their analysis was a part of a 9-month survey of the M87 galaxy utilizing Hubble’s near-UV Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS).
Up to now, all novae have been noticed in double-star methods consisting of a pink large star and a white dwarf companion. In these methods, the outer layers of the pink large are siphoned away by the white dwarf and accreted onto its floor. When the white dwarf has gathered sufficient hydrogen, the layer explodes in a “nova eruption,” and the cycle begins once more. When the staff noticed M87 utilizing Hubble’s COS, they discovered twice as many novae eruptions close to the 3000-light-year-long jet than within the galaxy itself in the course of the surveyed interval.
These findings suggest that there are twice as many nova-forming double-star methods close to the jet or that these methods erupt twice as usually as comparable methods elsewhere within the galaxy. One other risk is that the jet is heating the pink large stars in these binary methods, inflicting them to overflow additional and dump extra hydrogen onto the dwarf companion. Nonetheless, the researchers decided that this heating just isn’t vital sufficient to have this impact. As Lessing defined in an ESA press launch:
“We don’t know what’s happening, however it’s only a very thrilling discovering. This implies there’s one thing lacking from our understanding of how black gap jets work together with their environment… There’s one thing that the jet is doing to the star methods that wander into the encompassing neighborhood.
“Perhaps the jet one way or the other snowplows hydrogen gas onto the white dwarfs, inflicting them to erupt extra ceaselessly. Nevertheless it’s not clear that it’s a bodily pushing. It could possibly be the impact of the strain of the sunshine emanating from the jet. If you ship hydrogen sooner, you get eruptions sooner. One thing is perhaps doubling the mass switch fee onto the white dwarfs close to the jet.”
This isn’t the primary time astronomers have observed elevated ranges of exercise across the M87 jet. Shortly after Hubble launched in 1990, astronomers noticed the galaxy’s SMBH utilizing its first-generation Faint Object Digicam (FOC). These observations revealed “transient occasions” that could possibly be proof of novae, however the FOC’s view was too slim to check what was occurring between the jet and within the near-jet area. Due to the nine-month marketing campaign that relied on Hubble’s upgraded cameras (which have a wider view) and seen the jet’s setting each 5 days, the staff was capable of rely the novae alongside the jet’s trajectory.

The observations, which had been the deepest pictures of M87 ever taken, revealed 94 novae inside the M87 galaxy’s interior area. Stated co-author Michael Shara, the Curator of Astrophysics on the American Museum of Pure Historical past:
“The jet was not the one factor that we had been — we had been wanting on the total interior galaxy. When you plotted all identified novae on prime of M87 you didn’t want statistics to persuade your self that there’s an extra of novae alongside the jet. This isn’t rocket science. We made the invention just by wanting on the pictures. And whereas we had been actually stunned, our statistical analyses of the information confirmed what we clearly noticed.”
These observations affirm that the venerable Hubble nonetheless has the potential to disclose new and attention-grabbing issues in regards to the Universe. As well as, these findings present a chance for follow-up research to be taught extra about how relativistic jets might affect star methods extending effectively past their galaxies.
Additional Studying: ESA Hubble, The Astrophysical Journal



No comments! Be the first commenter?