*
We’ve identified the Universe is increasing for a very long time. The primary stable paper demonstrating cosmic enlargement was printed by Edwin Hubble in 1929, based mostly on observations made by Vesto Slipher, Milton Humason, and Henrietta Leavitt. Due to this, the speed of cosmic enlargement is named the Hubble fixed, or Hubble parameter, H0. From this parameter, you’ll be able to calculate issues such because the age of the Universe for the reason that Massive Bang, so understanding the worth of H0 is central to our understanding of recent cosmology.
Early on, the measured worth of the Hubble parameter diversified broadly. Hubble’s preliminary worth was on the order of 500 (km/s)/Mpc. By the Sixties, the worth settled right down to between 50 and 90 (km/s)/Mpc, the place it stayed for a lot of the twentieth century. It was troublesome to get extra exact as a result of our strategies of calculating it have been restricted. All of those have been based mostly on the cosmic distance ladder, which makes use of a collection of observations to calculate ever higher cosmic distances, every constructing on the earlier methodology. However prior to now few many years we received fairly good at it, and the Hubble worth appeared to settle round 70 (km/s)/Mpc. After that, issues began to get…problematic.
With satellites comparable to WMAP and Planck we began to get high-resolution maps of the cosmic microwave background. From fluctuations on this background we have now a brand new approach to measure H0 and get a price of 67 – 68 (km/s)/Mpc. On the identical time, observations of distant supernovae and the cosmic distance ladder pin down the worth to 73 – 75 (km/s)/Mpc. Each strategies are fairly exact, and but they fully disagree. This disagreement is now referred to as the Hubble rigidity downside, and it’s the most bothersome thriller in cosmology.
We aren’t positive what causes the Hubble rigidity. It would imply that a number of of our remark strategies are essentially flawed, or it would imply there’s something about darkish vitality and cosmic enlargement that we actually don’t perceive. However astronomers usually agree that one approach to deal with this thriller is to search for methods to measure H0 which are impartial of each the cosmic background and the cosmic distance ladder. One such methodology entails gravitational lensing.
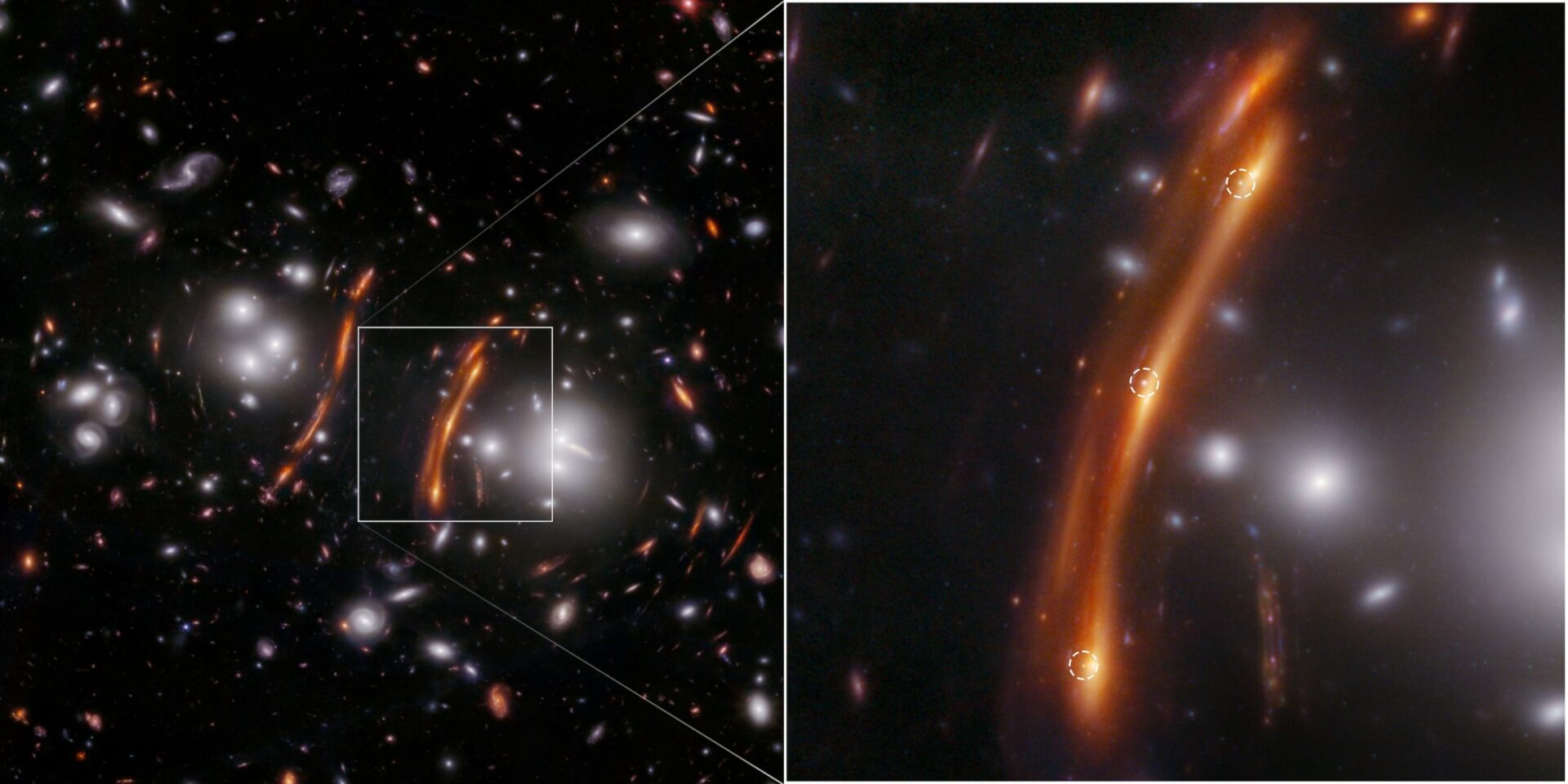
Gravitational lensing happens as a result of gravity warps area, that means that the trail of sunshine might be deflected by the presence of a big mass. So, for instance, if a distant galaxy occurs to be behind a more in-depth galaxy from our vantage level, we see a gravitationally distorted view of the distant galaxy and even a number of pictures of the galaxy. The attention-grabbing factor in regards to the a number of picture impact is that the sunshine from every picture travels a distinct path across the nearer galaxy, every with a distinct distance. For the reason that velocity of sunshine is finite this implies every picture provides us a view of the galaxy at totally different instances in historical past.
This doesn’t matter a lot for galaxies, however for supernovae it means gravitational lensing can allow us to observe the identical supernova a number of instances. By calculating the trail of every supernova picture we are able to decide the relative distance of every path, and by timing the looks of every picture we are able to decide the precise distance. This offers us a measurement that’s impartial of the cosmic distance ladder, giving us a brand new approach to measure the Hubble parameter. This methodology has been used a few instances, however the uncertainties of their Hubble values weren’t sufficiently small to deal with the Hubble rigidity. Nonetheless, a brand new examine utilizing this methodology is exact sufficient.
The examine relies on JWST pictures of a Sort Ia supernova named SN H0pe. It is likely one of the most distant supernovae ever noticed, and because of the less-distant galaxy cluster G165, the staff captured three lensed pictures of SN H0pe. With their timing, noticed brightness, and calculated paths, the staff calculated H0 to be 70 – 83 (km/s)/Mpc. This nonetheless has a better uncertainty than different strategies, however it agrees with the same old distance ladder methodology. It additionally clearly disagrees with the cosmic microwave background methodology.
Regardless of H0pe, the Hubble rigidity could be very actual. If something, this new consequence makes the difficulty much more troublesome. There’s something about cosmic enlargement we don’t perceive, and it’s now clear that higher observations won’t clear up this thriller on their very own.
Reference: Pascale, Massimo, et al. “SN H0pe: The First Measurement of H0 from a Multiply-Imaged Sort Ia Supernova, Found by JWST.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.18902 (2024).




No comments! Be the first commenter?