*
21 December would be the shortest day of 2024 within the northern hemisphere, midwinter day.
That is the day when the Solar’s annual journey by the
constellations of the
zodiac
reaches its most southerly level within the sky, within the constellation of
Capricornus at a declination of 23.5°S.
Today is counted by astronomers to
be the primary day of winter within the northern hemisphere.
Within the southern hemisphere, the Solar is above the horizon for longer
than on another day of the yr, and astronomers outline this to be the
first day of summer time.
On the solstice, the Solar seems overhead at midday when noticed from
areas on the tropic of Capricorn, at a latitude 23.5°S.
| Date | Dawn | Midday | Sundown | |
| 23 | Nov | 06:31 | 11:38 | 16:44 |
| 27 | Nov | 06:34 | 11:39 | 16:43 |
| 01 | Dec | 06:38 | 11:40 | 16:42 |
| 05 | Dec | 06:41 | 11:42 | 16:42 |
| 09 | Dec | 06:44 | 11:44 | 16:43 |
| 13 | Dec | 06:47 | 11:45 | 16:44 |
| 17 | Dec | 06:50 | 11:47 | 16:45 |
| 21 | Dec | 06:52 | 11:49 | 16:47 |
| 25 | Dec | 06:54 | 11:51 | 16:49 |
| 29 | Dec | 06:55 | 11:53 | 16:52 |
| 02 | Jan | 06:56 | 11:55 | 16:55 |
| 06 | Jan | 06:57 | 11:57 | 16:58 |
| 10 | Jan | 06:56 | 11:59 | 17:01 |
| 14 | Jan | 06:56 | 12:00 | 17:05 |
|
Dawn and sundown occasions for Los Angeles See extra… |
||||
Dawn and sundown occasions
The desk to the correct lists the dawn and sundown occasions in Los Angeles round
the solstice. At the moment of yr, midday – the second when the Solar seems highest within the sky
– strikes round a minute later every day.
This phenomenon is described by the
equation of time,
and is brought on by slight variations within the size of every
day relying on the time of yr.
In some months, days will be as much as 20 seconds longer or shorter
than 24 hours, in a predictable sample which repeats yearly. This arises from two results:
-
The speed of the Solar’s eastward motion by the constellations modifications over
the course of the yr. It’s quickest on the solstices, and slowest on the
equinoxes. -
The Earth’s orbit across the Solar shouldn’t be an ideal circle, however is barely
elliptical. Because of this its orbital velocity modifications by the yr.
Each these results very barely alter the speed of motion of the Solar throughout the sky, including
or subtracting just a few seconds from the time it takes to get from midday on sooner or later to midday the following day.
Clocks, nonetheless, proceed to run at a continuing price always of yr. Because of this, at these
occasions of yr when days are shorter than 24 hours, midday drifts earlier within the day. When days are
longer than 24 hours, the midday comes later every day.
In December, every photo voltaic day lasts fractionally longer than
24 hours, and so the time of midday strikes round a minute later every day.
The shift additionally impacts dawn and sundown occasions, and implies that the
newest dawn and earliest sundown don’t happen on the day of the solstice itself.
As an alternative, the earliest sundown happens a few weeks beforehand, and the newest dawn is a few weeks later.
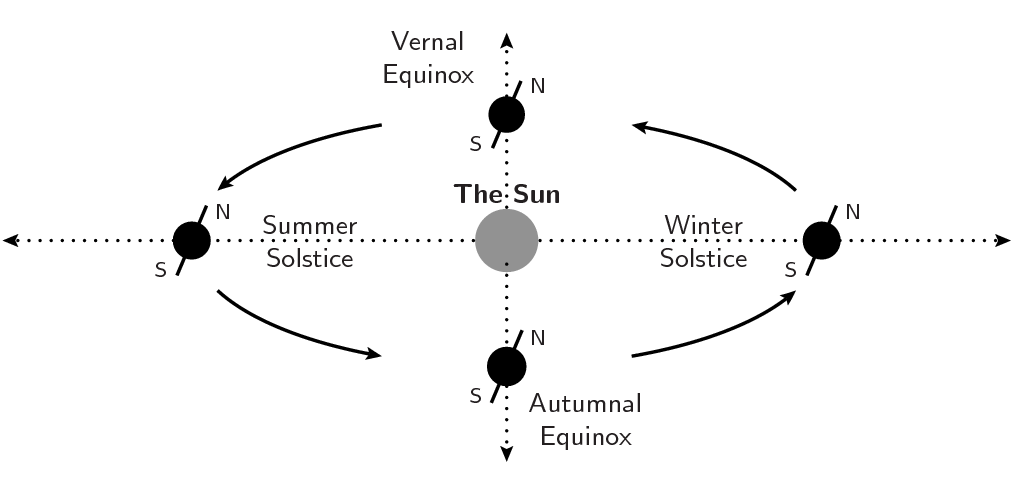
Solstice geometry
Solstices happen as a result of the axis of the Earth’s spin – its polar axis
– is tilted at an angle of 23.5° to the aircraft of its orbit across the
Solar.
The course of the Earth’s spin axis stays fastened in area because it circles
across the Solar, whereas the Earth’s sight line to the Solar strikes by the
constellations of the
zodiac.
Consequently, generally the Earth’s north pole is tilted in the direction of the Solar (in
June), and at different occasions it’s tilted away from it (in December). This offers rise
to the Earth’s seasons:
The date of the solstice
| 12 months | Time of solstice |
| 2020 | 21 Dec 01:55 PST |
| 2021 | 21 Dec 07:53 PST |
| 2022 | 21 Dec 13:43 PST |
| 2023 | 21 Dec 19:24 PST |
| 2024 | 21 Dec 01:20 PST |
| 2025 | 21 Dec 07:04 PST |
| 2026 | 21 Dec 12:53 PST |
| 2027 | 21 Dec 18:47 PST |
| 2028 | 21 Dec 00:26 PST |
The Earth orbits the Solar as soon as each 365.242 days, and that is the time
interval over which the cycle of solstices and equinoxes, and consequently all
the Earth’s seasons, repeat from one yr to the following.
In any yr which isn’t a intercalary year, the solstices happen roughly 5 hours and
48 minutes – just below 1 / 4 of a day – later from one yr to
the following.
This is the reason the seasons would drift later within the yr if it was not for an
further day being inserted inserted into each fourth yr on 29 February.
The chart under exhibits the time when the December solstice falls in
annually. The gradual drift of the four-year cycle earlier within the month is due
to the equinoxes repeating 12 minutes lower than 1 / 4 of a day later every
yr.
Within the Gregorian calendar, that is fastened by omitting leap years in three out of
each 4 century years, e.g. 1700, 1800 and 1900, however not 2000.
The date of Christmas
Christmas borrows its date from historical pagan midwinter festivals, although
within the trendy calendar Christmas now falls just a few days after astronomical
midwinter.
This anomaly has come about as a result of the system of leap days that are generally
inserted into our calendar on February 29 was solely refined to its current kind
by the Gregorian calendar reforms of the sixteenth century. Earlier than this, the typical
size of every yr didn’t fairly match the time frame with which the
seasons repeat – 365.2422 days – and so the seasons drifted by
the yr by a small quantity every century. So, within the distant previous, the winter
solstice occurred just a few days later than it does at the moment.
The 2024 solstice
The precise place of the Solar when it reaches its most southerly declination in
2024 might be (J2000.0 coordinates):
| Object | Proper Ascension | Declination | Constellation | Angular Measurement |
| Solar | 17h58m | 23°26’S | Sagittarius | 32’31” |
The sky
on 21 Dec 2024
Supply
The circumstances of this occasion have been computed utilizing the DE430 planetary ephemeris revealed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
This occasion was robotically generated by looking the ephemeris for planetary alignments that are of curiosity to newbie astronomers, and the textual content above was generated based mostly on an estimate of your location.
Picture credit score
The Earth, as seen by the Apollo 17 astronauts. © NASA





No comments! Be the first commenter?