*
NASA performs first plane accident investigation on one other world
by Employees Writers
Pasadena CA (JPL) Dec 13, 2024
Engineers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and AeroVironment are finishing an in depth evaluation of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter’s ultimate flight on Jan. 18, 2024, which will likely be printed within the subsequent few weeks as a NASA technical report. Designed as a expertise demonstration to carry out as much as 5 experimental check flights over 30 days, Ingenuity was the primary plane on one other world. It operated for nearly three years, carried out 72 flights, and flew greater than 30 instances farther than deliberate whereas accumulating over two hours of flight time.
The investigation concludes that the lack of Ingenuity’s navigation system to supply correct information throughout the flight possible prompted a series of occasions that ended the mission. The report’s findings are anticipated to learn future Mars helicopters, in addition to different plane destined to function on different worlds.
Remaining Ascent
Flight 72 was deliberate as a quick vertical hop to evaluate Ingenuity’s flight techniques and {photograph} the realm. Knowledge from the flight reveals Ingenuity climbing to 40 toes (12 meters), hovering, and capturing pictures. It initiated its descent at 19 seconds, and by 32 seconds the helicopter was again on the floor and had halted communications. The next day, the mission reestablished communications, and pictures that got here down six days after the flight revealed Ingenuity had sustained extreme injury to its rotor blades.
What Occurred
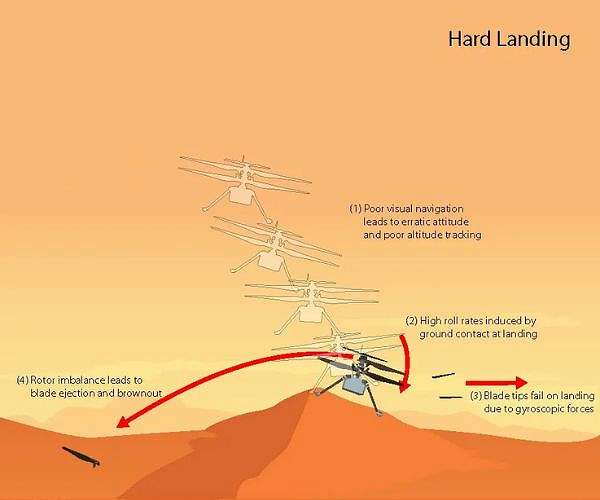
“When operating an accident investigation from 100 million miles away, you have no black containers or eyewitnesses,” stated Ingenuity’s first pilot, Havard Grip of JPL. “Whereas a number of situations are viable with the out there information, now we have one we consider is most probably: Lack of floor texture gave the navigation system too little info to work with.”
The helicopter’s imaginative and prescient navigation system was designed to trace visible options on the floor utilizing a downward-looking digicam over well-textured (pebbly) however flat terrain. This restricted monitoring functionality was greater than adequate for finishing up Ingenuity’s first 5 flights, however by Flight 72 the helicopter was in a area of Jezero Crater crammed with steep, comparatively featureless sand ripples.
One of many navigation system’s major necessities was to supply velocity estimates that might allow the helicopter to land inside a small envelope of vertical and horizontal velocities. Knowledge despatched down throughout Flight 72 reveals that, round 20 seconds after takeoff, the navigation system could not discover sufficient floor options to trace.
Images taken after the flight point out the navigation errors created excessive horizontal velocities at landing. Within the most probably state of affairs, the arduous impression on the sand ripple’s slope prompted Ingenuity to pitch and roll. The fast angle change resulted in hundreds on the fast-rotating rotor blades past their design limits, snapping all 4 of them off at their weakest level – a few third of the best way from the tip. The broken blades prompted extreme vibration within the rotor system, ripping the rest of 1 blade from its root and producing an extreme energy demand that resulted in lack of communications.
Down however Not Out
Though Flight 72 completely grounded Ingenuity, the helicopter nonetheless beams climate and avionics check information to the Perseverance rover about as soon as every week. The climate info may benefit future explorers of the Pink Planet. The avionics information is already proving helpful to engineers engaged on future designs of plane and different autos for the Pink Planet.
“As a result of Ingenuity was designed to be reasonably priced whereas demanding large quantities of pc energy, we turned the primary mission to fly industrial off-the-shelf cellphone processors in deep house,” stated Teddy Tzanetos, Ingenuity’s mission supervisor. “We’re now approaching 4 years of steady operations, suggesting that not every part must be larger, heavier, and radiation-hardened to work within the harsh Martian atmosphere.”
Impressed by Ingenuity’s longevity, NASA engineers have been testing smaller, lighter avionics that may very well be utilized in automobile designs for the Mars Pattern Return marketing campaign. The info can also be serving to engineers as they analysis what a future Mars helicopter may appear to be – and do.
Throughout a Wednesday, Dec. 11, briefing on the American Geophysical Union’s annual assembly in Washington, Tzanetos shared particulars on the Mars Chopper rotorcraft, an idea that he and different Ingenuity alumni are researching. As designed, Chopper is roughly 20 instances heavier than Ingenuity, may fly a number of kilos of science gear, and autonomously discover distant Martian areas whereas touring as much as 2 miles (3 kilometers) in a day. (Ingenuity’s longest flight was 2,310 toes, or 704 meters.)
“Ingenuity has given us the boldness and information to examine the way forward for flight at Mars,” stated Tzanetos.
For extra details about Ingenuity right here
Associated Hyperlinks
Mars Helicopter Updates
Mars Information and Info at MarsDaily.com
Lunar Goals and extra




No comments! Be the first commenter?