*
NASA
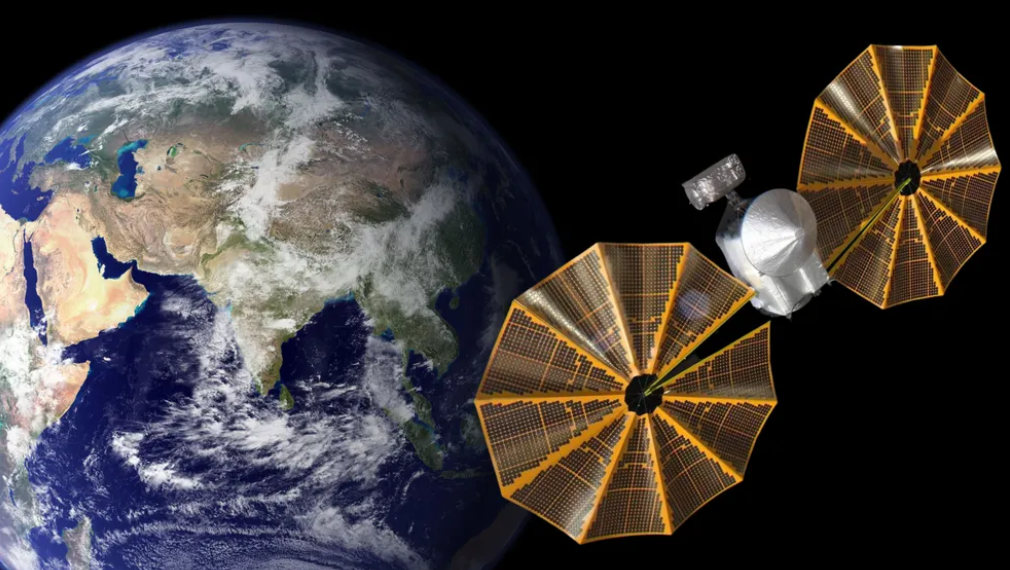
An thrilling mission is about to re-visit our honest planet this week on Thursday night time/Friday morning, as NASA’s Lucy spacecraft passes Earth in a bid to choose up pace. The gravitational help could have Lucy fly by round 11:15 p.m. EST on December twelfth (4:15 Common Time on Friday, December thirteenth). The closest method will happen 354 kilometers (220 miles) above the Pacific Ocean simply west off the coast of California.
Launched in October 2021, Lucy is headed to discover the 2 camps of asteroids that orbit stably on both aspect of Jupiter: the Greek camp situated at Jupiter’s L4 Lagrange level (forward of the planet on its orbit) and the opposing Trojan camp on the L5 level behind Jupiter. The mission will go to a complete of 11 asteroids (three main-belt asteroids and eight Trojans).
To get there takes some sophisticated orbital gymnastics, and this flyby previous Earth is the second of three. The flyby will enhance the spacecraft’s velocity relative to the Solar by 7.3 kilometers per second (16,000 mph). After crossing the Moon’s orbit 34 hours previous to the flyby, the spacecraft will cross the skies above North America in simply seven minutes, transferring at 14.8 km/s relative to Earth.

NASA
Threading Earth’s Shadow
Sadly, the spacecraft can be a bashful one on this move, because it hits Earth’s shadow only one minute previous to its closest method above the floor. That can make it tough to see. However issues enhance a bit on shadow egress, which happens 20 minutes later at 4:34 UT; the southeastern U.S., western Europe, western Africa, and japanese South America might have a very good view of Lucy as a +Seventh-magnitude binocular object. By that point, it is going to be greater than 6,920 kilometers away. Though this places the spacecraft past low-Earth orbit, it should nonetheless be inside to geosynchronous orbit.
Whereas observers in Hawai’i might see Lucy zip by the twilight sky simply earlier than shadow ingress, southern Atlantic space observers are favored at egress because of the anticipated angle of the spacecraft’s monumental photo voltaic panels, which is able to nonetheless be reflecting daylight. Observers in North America and Europe can be seeing the panels edge-on or from the again.
Whereas Tony Dunn (San Francisco State College) does not count on to see the flyby nicely from his location, he provides, “I’ll must be joyful merely understanding that it’s just a few hundred kilometers above my head (!)”
NASA’s Lucy mission will go to Earth this weekend for a gravity help that can ship it to Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids. At its closest, it should move about 250 miles above California, much like the altitude of the ISS. However Lucy can be in Earth’s shadow then.
[image or embed]
— Tony Dunn (@tony873004.bsky.social) December 9, 2024 at 4:09 PM
Easy methods to Discover Lucy
You should utilize NASA JPL’s Horizons ephemeris generator to create an inventory of minute-by-minute proper ascension and declination search coordinates to your web site. For instance, from my very own location in Miami, Florida, I count on a view of the receding spacecraft in Most cancers, the Crab — simply south of Mars. I’d deal with the search much like looking forward to a satellite tv for pc that is beneath bare eye brightness: discover a vivid mounted star within the discipline utilizing binoculars and hold watch on the appointed time to see Lucy slide by.

David Dickinson / Stellarium
Throughout the earlier flyby, in 2022, controllers used the chance to check and calibrate devices onboard Lucy, a marketing campaign that went off with out a hitch. This time, there will not be a repeat. “We’re not planning on doing any observations in the course of the flyby,” says principal investigator Harold Levison (Southwest Analysis Institute)
Astronomer Gianluca Masi tracked Lucy on its first Earth flyby, and can once more host a dwell broadcast through the Digital Telescope Venture beginning at 11:30 p.m. EST December twelfth / 4:30 UT December thirteenth. You may also observe NASA’s social media hashtag #SpotTheSpacecraft this week.

Gianluca Masi / Digital Telescope Venture
What’s subsequent for Lucy
The mission already made its first flyby previous asteroid 152830 Dinkinesh on November 1, 2023 revealing that the asteroid possesses a tiny moonlet, later named Selam. Selam turned out to be a small contact binary pair, the primary such pair seen orbiting an asteroid.

NASA / GSFC / SwRI / John Hopkins APL / NOIRLab
Now, this move will ship Lucy from a two-year orbit across the Solar to a six-year orbit, which takes it to its subsequent goal: the main-belt asteroid 52246 Donaldjohanson. Lucy will move 922 kilometers from the asteroid on April 20, 2025. Then, on August 12, 2027, Lucy will attain its first “Greek Camp” asteroid, 3548 Eurybates.
Lucy will truly revisit Earth a 3rd and last time on December 26, 2030, which is able to ship it to the Trojan camp on the opposite aspect of Jupiter in its orbit. Lucy’s eighth and final goal of its mission is the 617 Patroclus-Menoetius pair in 2033.