*
A current research discovered that SpaceX’s Starlink V2-mini satellites emit extra radio waves, probably interfering with radio astronomy.
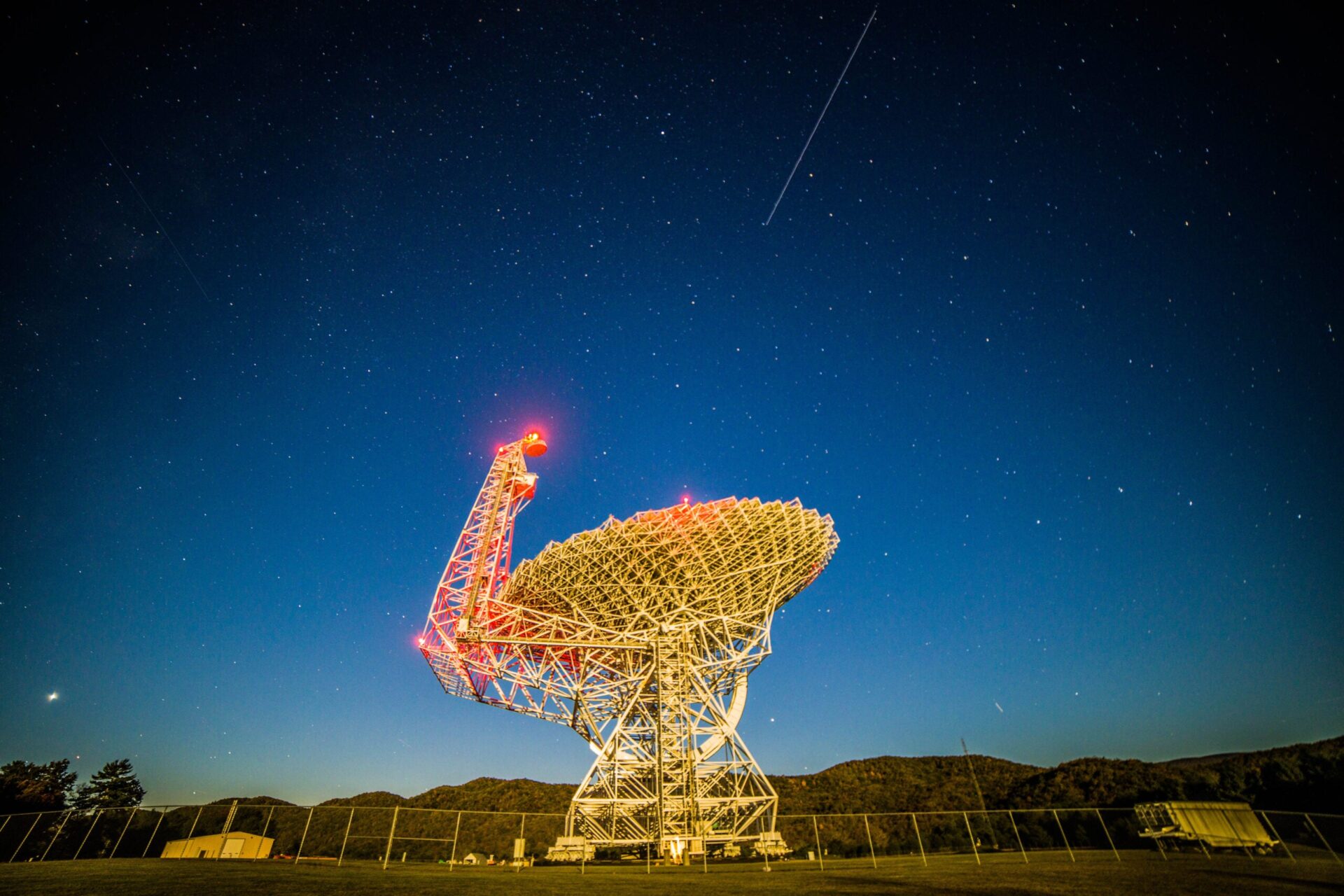
The Inexperienced Financial institution Telescope in West Virginia lies on the coronary heart of the Nationwide Radio Quiet Zone, an space the place radio transmissions — together with wifi and cell telephones — are closely restricted. Credit score: NSF/AUI/NSF GBO/J. Seymour
Researchers utilizing the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) radio telescope in Europe have found the second era of Starlink satellites emit larger ranges of radio waves that would pose a critical danger to radio astronomy.
This concern of radio-wave emission is along with the daylight that Starlink and different satellites replicate, which will be seen to the bare eye and depart mild streaks on optical photographs.
In observations taken over the summer time, Starlink’s V2-mini — an upgraded mannequin of its internet-providing satellites — emits as much as 32 instances extra unintended electromagnetic radiation (UEMR) than its predecessor. The LOFAR radio telescope, composed of a number of antennas throughout Europe and managed by the Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy (ASTRON), tracked satellites on July 19 over the course of two one-hour periods. The outcomes, printed within the journal Astronomy & Astrophysicson Sept. 18, discovered that the objects emitted extra highly effective radio waves than the earlier era. The problem is exacerbated by the truth that V2-mini satellites function at a decrease orbit than earlier Starlink satellites.
In keeping with LOFAR lead researcher Cees Bassa in an ASTRON information launch, these satellites are about 10 hundreds of thousands instances brighter in radio waves than any faint objects LOFAR may find. “This distinction is much like the faintest stars seen to the bare eye and the brightness of the complete Moon. Since SpaceX is launching about 40 second-generation Starlink satellites each week, this downside is changing into more and more worse.”
SpaceX started launching the V2-mini era of satellites early final 12 months as a part of the corporate’s Starlink constellation, which provides high-speed web entry throughout the globe. The satellites incorporate new measures to scale back their reflectivity, serving to to mitigate their affect on optical astronomy and naked-eye observations. In a launch in 2023, the corporate highlighted its work with astronomers, saying it has “prioritized collaboration with astronomers and scientists to mitigate the affect of Starlink satellite tv for pc streaks on their observations.” Nonetheless, the brand new outcomes present there may be extra work to be accomplished to decrease their affect on radio astronomy.
SpaceX didn’t reply to requests for remark.
SpaceX has additionally labored with the U.S. Nationwide Science Basis and Nationwide Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) to scale back their affect on the sector, having signed a coordination settlement in 2019. In experiments performed since 2021 on the Very Giant Array in New Mexico, SpaceX and the NRAO have labored on strategies to coordinate operations in order that Starlink satellites can steer their transmission beams away from working radio telescopes. Nonetheless, the radio emission detected on this new research issues electromagnetic radiation that leaks out from satellites unintentionally.
The LOFAR research said that there are methods to maintain these satellites from interfering with radio telescopes. These actions embrace elevating consciousness, advocating for radio quiet zones, and stricter trade rules.
The research states that with this new info, there may be hope that SpaceX and Starlink will work to mitigate UEMR and its affect on astronomy sooner or later.




No comments! Be the first commenter?